The goal of this project was to evaluate whether the Stacked Hourglass Network (a state-of-the-art deep neural network) trained on human data would generalize to also predict the pose of Atlas (Boston Dynamics’ humanoid robot). Given the similarity between the structure of Atlas and a human, this project also was a means to provide interpretability to the Stacked Hourglass Network, elucidating the features it may use for pose detection. The code for this project is available here and a final report can be found here.
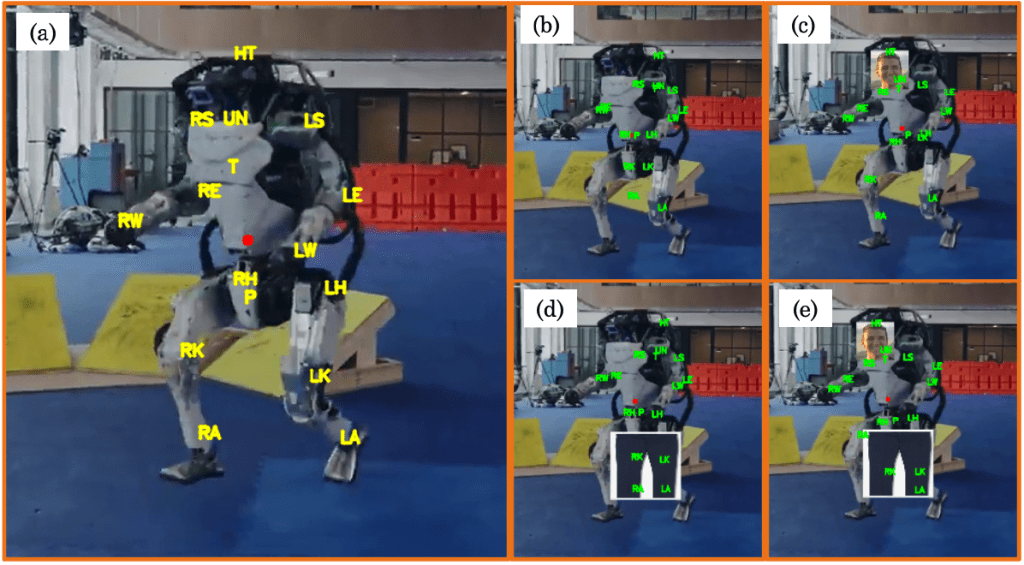
The first step in the process was to parse a video of Atlas doing parkour into frames. To be able to evaluate the performance of the network on Atlas, we had to write a script where we could manually label the joints of Atlas. The picture below shows a labeled image of Atlas.
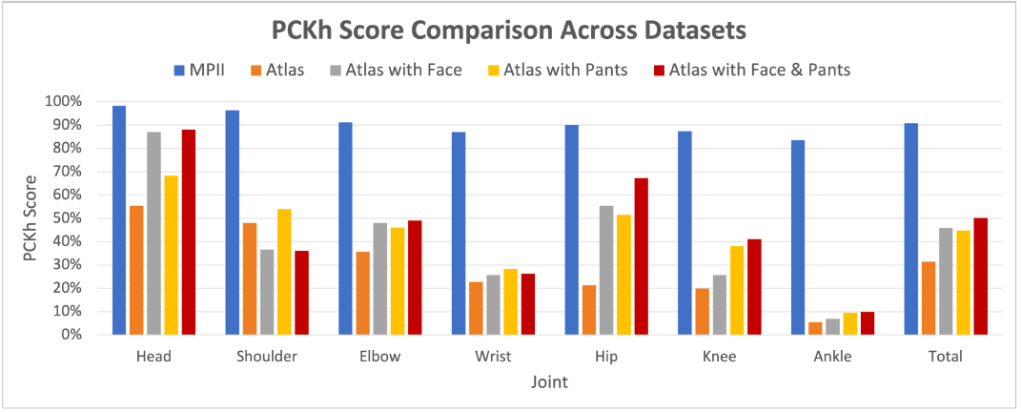
We noticed that the network performed poorly on just the images of Atlas, indicating that it must use distinctly human features to predict pose. To test this hypothesis we programmatically added pants and a face onto Atlas, which increased the performance of the network! This indicated that the network identified features such as clothing and facial structures to then infer pose, which provides added interpretability to what was a black box.
For more details, see the paper below: